Selecting the right submersible slurry pump is one of the most crucial decisions for industries handling abrasive, high-solid-content fluids. From mining and dredging to wastewater treatment and construction, these pumps play a vital role in maintaining efficiency and minimizing downtime. Understanding how they work, their design variations, and the factors that influence selection helps engineers and procurement teams make informed choices that directly impact project performance and long-term cost savings.
What is a Submersible Slurry Pump?
A submersible slurry pump is a heavy-duty pump designed to operate while fully submerged in the fluid it is handling. Unlike conventional pumps that sit outside the fluid source, submersible slurry pumps are installed directly into the slurry pit, sump, or water body, allowing them to efficiently move high-density mixtures of solids and liquids. The working principle is straightforward yet robust: the pump’s motor is sealed to prevent liquid ingress, and the impeller creates a strong suction force that transports abrasive slurries, sediments, and solid-laden fluids through the discharge pipeline. This design eliminates the need for priming and reduces the risk of air binding, making these pumps highly reliable in demanding environments.
One of the key distinctions between a submersible slurry pump and other pump types lies in its installation and operational setup. Horizontal slurry pumps, for example, require a dry installation and suction piping, which can add complexity in confined spaces. Vertical slurry pumps extend downward into the pit but still require significant support structures and often occupy more space above ground. Self-priming pumps, while convenient for surface installation, are not ideal for extremely abrasive or dense slurries due to wear limitations. In contrast, submersible slurry pumps are fully immersed, compact in design, and directly handle slurries at the source, minimizing suction losses and simplifying deployment.
The advantages of using submersible slurry pumps become clear in high-solids and abrasive applications. Because the pump sits at the bottom of the pit or directly in the slurry, it can process heavier mixtures without the limitations of suction lift. This makes it ideal for mining tailings ponds, dredging operations, construction dewatering, and wastewater facilities handling grit and sludge. Their rugged construction—often featuring wear-resistant impellers, hardened casings, and advanced sealing systems—ensures a longer service life in abrasive environments. Additionally, modern designs such as the electric submersible slurry pump offer energy efficiency and ease of operation, supporting continuous duty even in the harshest conditions.
Types of Submersible Slurry Pumps
Submersible slurry pumps are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different pump configurations are designed to handle specific materials, flow conditions, and operating environments. Understanding the main types helps engineers and project managers match the right pump to the demands of their application.
Standard Submersible Slurry Pump
This is the most widely used option for heavy-duty operations. Built with robust impellers and wear-resistant casings, standard models are engineered to handle abrasive slurries with high concentrations of solids. They are commonly deployed in mining pits, dredging projects, and construction dewatering.
Electric Submersible Slurry Pump
The electric submersible slurry pump has gained popularity for its efficiency and ease of operation. Powered by sealed electric motors, these pumps deliver consistent performance in continuous-duty applications. Their compact design eliminates the need for suction piping, making them ideal for confined spaces and remote projects where quick installation is critical.
Material Variations
Submersible slurry pumps can also be classified by their construction materials. Cast-iron pumps are suitable for general slurry handling. At the same time, high-chrome alloys offer extended wear life in highly abrasive conditions. Stainless steel builds are used when corrosion resistance is essential, such as in chemical or wastewater applications.
Quick Comparison of Pump Types and Applications
| Pump Type | Best For | Key Benefit |
| Standard Submersible Slurry Pump | Mining, dredging, heavy construction | Rugged design for abrasive slurries |
| Electric Submersible Slurry Pump | Continuous duty, remote installations | Energy efficiency and easy deployment |
| High-Chrome Alloy Build | Sand, gravel, abrasive tailings | Extended wear resistance |
| Stainless Steel Build | Corrosive or chemical-laden slurries | Superior corrosion protection |
Key Factors in Pump Selection

Choosing the right submersible slurry pump involves more than just capacity and price. Every slurry environment is unique, and the pump must be tailored to the material properties, site conditions, and performance demands of the project. Below are the most critical factors engineers and procurement teams should evaluate when specifying submersible slurry pumps or considering an electric submersible slurry pump for continuous-duty applications.
1. Nature of the Slurry
- Solids Size and Concentration: Larger, more abrasive solids require pumps with high-chrome impellers and vortex designs to minimize wear. Fine particles in high concentrations demand high efficiency and clog-resistant flow paths.
- Abrasiveness and Corrosiveness: Tailings, sand, and gravel are highly abrasive, while wastewater and chemical slurries may be corrosive. Material compatibility—such as hardened alloys or stainless steel—ensures longer service life.
2. Operating Environment
- Depth of Submergence: The pump’s design should match the required depth and submersion pressure. Fully submersible units handle deep pits without suction limitations.
- Site Conditions: Harsh settings, such as acidic water, high temperatures, or confined construction sites, can influence motor protection, cooling, and overall build quality.
3. Performance Parameters
- Flow Rate: Correctly sizing the pump to meet the project’s required gallons per minute (GPM) or cubic meters per hour prevents bottlenecks and energy waste.
- Total Dynamic Head (TDH): Evaluating static head, friction losses, and discharge pressure is crucial for pump longevity and efficiency.
- Efficiency Considerations: In applications where uptime is critical, electric submersible slurry pumps deliver consistent performance with lower energy consumption compared to surface-driven alternatives.
4. Power Options
- Electric Drive: Reliable, clean, and well-suited for continuous operations where grid power is available. Electric submersible slurry pumps are often chosen for their efficiency and reduced maintenance needs.
- Hydraulic Drive: A better fit for remote or mobile dredging projects where electric power is limited. Offers flexibility but requires additional hydraulic systems and monitoring.
Design Features to Look For
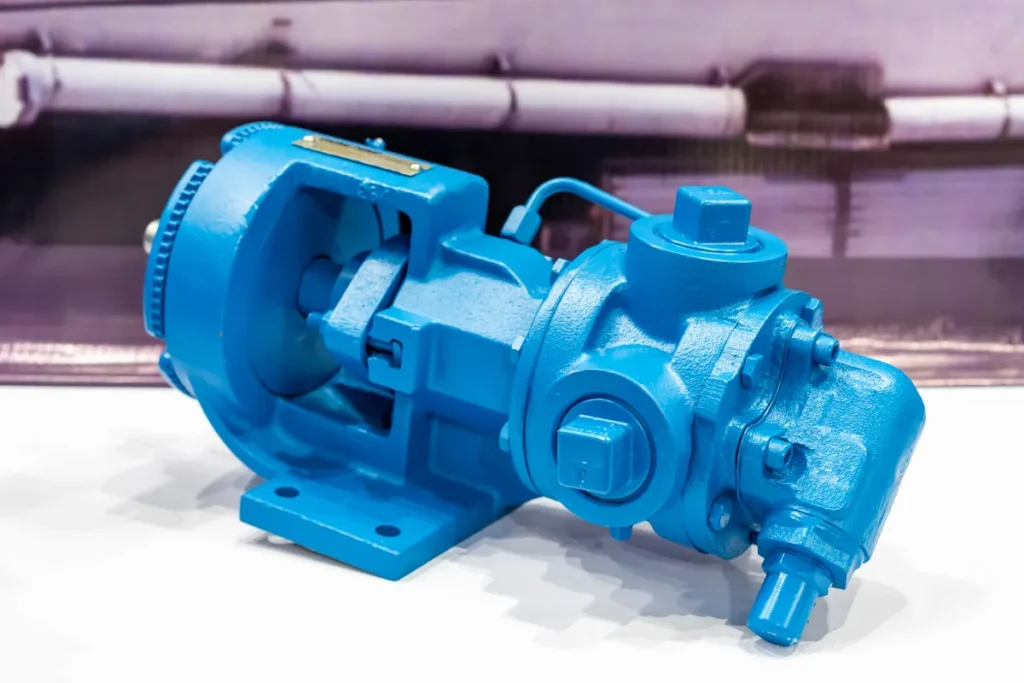

When evaluating a submersible slurry pump, design features are just as important as flow capacity or power. The right engineering choices can extend service life, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. Below are the core elements engineers and procurement teams should consider when comparing submersible slurry pumps and electric submersible slurry pumps.
Impeller Types
- Open Impeller: Best suited for handling larger solids and high-viscosity slurries, offering clog resistance but with slightly lower efficiency.
- Closed Impeller: Provides higher efficiency for fine-particle slurries but is less tolerant of oversized solids.
- Vortex Impeller: Ideal for abrasive and highly contaminated fluids, this impeller creates a whirlpool effect that reduces wear on itself.
Wear-Resistant Materials
- Pumps designed for abrasive duties often feature high-chrome alloys, hardened steel, or tungsten coatings to withstand continuous impact and erosion.
- Stainless steel constructions are essential where corrosion is a concern, such as in wastewater, chemical, or marine applications.
Motor Protection
- Double mechanical seals and seal failure detection systems prevent slurry ingress into the motor.
- Integrated thermal protection safeguards against overheating in demanding, continuous operations.
- Options for oil-cooled or water-cooled motors ensure reliability under varying site conditions.
Monitoring and Control Systems
- Modern electric submersible slurry pumps often integrate with smart monitoring solutions, including vibration sensors, bearing temperature gauges, and remote telemetry.
- These systems allow predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and extending pump life.
Ease of Maintenance
- Features such as replaceable wear liners, modular casing designs, and accessible inspection ports simplify maintenance tasks.
- Quick-disconnect cabling and plug-and-play motor assemblies minimize field service time, especially in remote dredging or mining locations.
Advantages of Electric Submersible Slurry Pumps

Among the different designs available, the electric submersible slurry pump has become a preferred choice in industries where efficiency, reliability, and ease of installation are top priorities. Its design integrates the motor and pump into a single sealed unit, offering several advantages over traditional slurry pumping systems.
Compact Installation
Because the pump is fully submerged, there is no need for suction piping or priming equipment. This allows for a smaller installation footprint, making electric submersible slurry pumps ideal for projects with limited space, such as underground mines, construction sites, or wastewater treatment pits.
Continuous Operation
Electric motors provide steady and reliable power, enabling the pump to run for extended periods without interruption. This continuous-duty capability is critical in demanding environments where downtime translates directly into lost productivity and higher operating costs.
Energy Efficiency
Electric submersible slurry pumps are designed to minimize hydraulic losses and reduce energy consumption. By eliminating suction lift limitations and pumping the slurry directly at the source, they achieve greater efficiency compared to many surface-mounted alternatives.
Reduced Maintenance
With fewer external components such as drive shafts, couplings, and alignment systems, electric submersible slurry pumps simplify maintenance. The sealed design protects the motor from slurry ingress, while wear-resistant materials and mechanical seals extend service life in abrasive applications.
Environmental Benefits
By being directly submerged, these pumps reduce noise levels compared to surface-mounted equipment. They also lower the risk of leakage and spillage, supporting safer and more environmentally responsible operations in industries such as mining, dredging, and municipal wastewater management.
Common Applications of Submersible Slurry Pumps
The versatility of a submersible slurry pump makes it a valuable asset across multiple industries. By operating directly in the slurry, these pumps handle high concentrations of solids and abrasive materials that would quickly wear out conventional pumping equipment. Both standard and electric submersible slurry pumps are applied in sectors where reliability and performance are critical.
Mining and Mineral Processing
In mining operations, submersible slurry pumps are used to transport tailings, process slurries, and remove sediment from pits. Their ability to withstand abrasive materials such as sand, gravel, and ore fines makes them indispensable for mineral processing facilities.
Dredging and Marine Projects
From riverbed and harbor dredging to sand reclamation, submersible slurry pumps provide efficient sediment removal. Their submersible design eliminates suction limitations, allowing them to easily move large volumes of silt, sludge, and coarse particles.
Construction and Tunneling
On construction sites, especially in tunneling or foundation projects, groundwater often mixes with soil and debris to form abrasive slurries. Submersible slurry pumps are used for site dewatering, slurry transport, and maintaining safe working conditions.
Municipal and Wastewater Treatment
In municipal wastewater plants, pumps are deployed for sludge handling, grit removal, and sediment transfer. The electric submersible slurry pump is especially popular in these applications due to its continuous-duty efficiency and low maintenance needs.
Energy and Oil & Gas
Submersible slurry pumps also play a role in the energy sector, handling drilling mud, sand-laden water, and sediment control in oil & gas operations. Their robust construction supports long-term performance in harsh, high-demand environments.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations

Even the most durable submersible slurry pump requires proper care to ensure reliable long-term performance. A well-planned maintenance strategy minimizes downtime, protects against premature wear, and maximizes return on investment. Whether using standard models or an electric submersible slurry pump, the following practices are essential.
Proper Installation
Correct setup is the foundation of pump reliability. Pumps must be positioned at the correct depth and angle to avoid cavitation and ensure smooth slurry flow. Electrical connections and cabling should be adequately sealed to prevent water ingress and corrosion.
Regular Inspections
Routine checks help identify potential issues before they escalate and become more severe. Engineers should inspect impellers, wear liners, and seals for signs of erosion, as slurry environments are inherently abrasive. Monitoring vibration levels and noise changes can also serve as early indicators of mechanical stress.
Seal and Bearing Care
Seals and bearings are among the most critical components in submersible slurry pumps. Regular lubrication and timely replacement prevent slurry leakage into the motor housing, thereby extending pump service life. For electric models, built-in seal failure sensors add an extra layer of protection.
Wear-Part Replacement
Components such as impellers, liners, and casings experience high wear in abrasive slurries. Having spare parts readily available and a proactive replacement schedule helps maintain consistent pumping performance.
Predictive Monitoring
Modern electric submersible slurry pumps can be equipped with smart monitoring systems that track operating conditions in real time. Parameters such as motor temperature, seal pressure, and vibration can be analyzed to predict failures before they occur, allowing for planned maintenance rather than costly emergency repairs.
How to Match Pump to Project Needs

Selecting the right submersible slurry pump requires a structured approach. Every project has unique demands—from slurry composition to site conditions—and matching the pump correctly prevents downtime, reduces operating costs, and ensures long-term performance. Whether specifying a standard or electric submersible slurry pump, the following steps provide a clear framework for decision-making.
Step 1: Analyze the Slurry
- Measure solids’ size, percentage by volume, and abrasiveness.
- Identify corrosive elements that may require stainless steel or special coatings to prevent corrosion.
Step 2: Determine Flow and Head Requirements
- Calculate the required flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM) or cubic meters per hour.
- Establish total dynamic head (TDH), factoring in lift height, discharge line length, and friction losses.
Step 3: Assess Site Conditions
- Confirm the depth of submergence and available footprint for installation.
- Evaluate temperature, pH, and potential for confined-space challenges.
- Check power availability to determine whether to use an electric or hydraulic drive.
Step 4: Align Pump Materials and Design
- Match impeller type (open, closed, vortex) to slurry particle size.
- Select wear-resistant alloys for abrasive slurries, or stainless steel for corrosive applications.
Step 5: Consider Maintenance and Monitoring
- Select pumps with replaceable liners, accessible inspection ports, and seal monitoring capabilities.
- For continuous operations, electric submersible slurry pumps equipped with smart telemetry provide predictive maintenance and minimize downtime.
Step 6: Create a Procurement Checklist
- Slurry characteristics
- Flow and head requirements
- Site conditions
- Power options
- Material compatibility
- Maintenance and monitoring features
Final Insights on Submersible Slurry Pump Selection
Choosing the right submersible slurry pump—whether a standard or electric submersible slurry pump—is ultimately about aligning equipment capabilities with the demands of your project. By considering slurry characteristics, performance requirements, material compatibility, and maintenance strategies, you can ensure reliability and maximize ROI. At Virginia Dredging, we bring technical expertise and practical experience to help clients select the right pumping solutions for their unique needs. Contact us today to explore how we can support your next dredging or slurry management project.